Geothermal Heat Pump vs Gas Furnace: If you are looking for the best heating and cooling system for your home, you might be wondering whether you should choose a geothermal heat pump or a gas furnace. Both systems have pros and cons, and the best option for you depends on several factors, such as your climate, budget, and preferences.
Gas Furnaces Rely on the combustion of natural gas to generate heat.
In this article, we will compare and contrast the two systems in terms of their performance, environmental impact, installation and maintenance costs, and tax credits and incentives. By the end of this article, you will better understand the differences and benefits of geothermal heat pumps and gas furnaces, and you will be able to make an informed decision for your home.
What is a Geothermal Heat Pump?
Table of Contents
ToggleGeothermal heat pumps (GHPs) are an efficient and eco-friendly way to heat and cool your home. GHPs operate by circulating a liquid, typically water or antifreeze, through a loop of underground pipes where the temperature remains constant throughout the year. Depending on the season, the liquid either absorbs or releases heat from the ground and transfers it to a heat exchanger in your home. The heat exchanger distributes warm or cool air through ducts or radiators to maintain your desired temperature. You can read our detailed guide on the benefits of geothermal heat pumps.
Compared to other heating and cooling options, GHPs have the lowest operational cost and are significantly more efficient, generating 5 units of heat per 1 unit of electricity used. They are more cost-effective than running a natural gas furnace or an electric heat pump. GHPs are the clear winner when it comes to heating your home.
What is a Gas Furnace?
A gas furnace is a system that burns natural gas to produce heat for your home. It consists of a burner, a heat exchanger, a blower, and a vent. The burner ignites the gas and sends it to the heat exchanger, where it heats the air. The blower then pushes the warm air through ducts to your rooms while the vent expels the combustion byproducts, such as carbon monoxide and water vapor, to the outside.
Don’t forget to learn more about Winter Furnace Maintenance: Keep Your Heating System In Top Shape.
High-efficiency gas furnaces burn natural gas, an abundant natural resource, to create heat by burning fossil fuels. This process requires an external source of energy that comes from the same arena as geothermal heat pumps: the ground beneath our feet. This external energy source allows high-efficiency gas furnaces to generate heat more effectively and efficiently.
Understanding Geothermal Heat Pump vs Gas Furnace Easily
| Geothermal Heat Pump (GHP) | Gas Furnace |
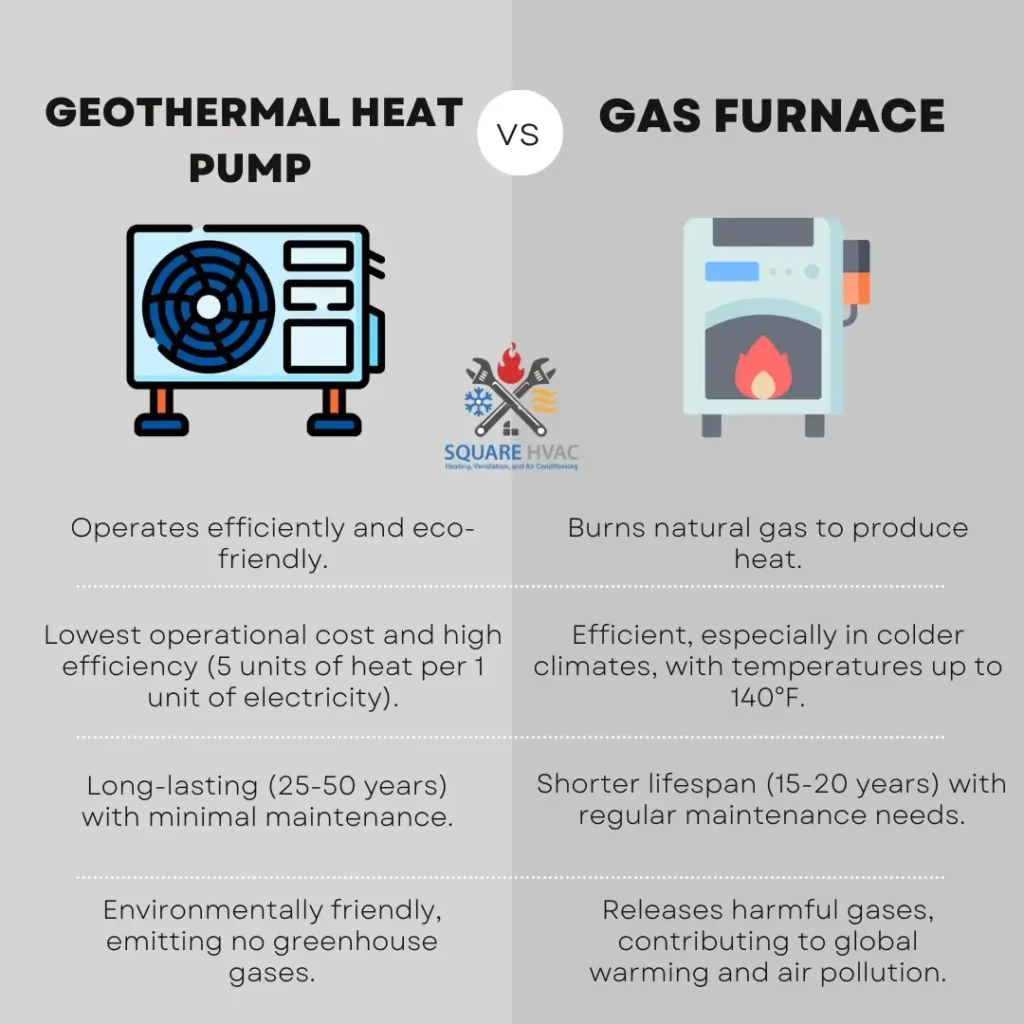
| Operates efficiently and eco-friendly. | Burns natural gas to produce heat. |
| Circulates liquid in underground pipes for consistent temperature. | Utilizes a burner, heat exchanger, blower, and vent for air heating. |
| Lowest operational cost and high efficiency (5 units of heat per 1 unit of electricity). | Efficient, especially in colder climates, with temperatures up to 140°F. |
| Environmentally friendly, emitting no greenhouse gases. | Releases harmful gases, contributing to global warming and air pollution. |
| Long-lasting (25-50 years) with minimal maintenance. | Shorter lifespan (15-20 years) with regular maintenance needs. |
Geothermal Heat Pump vs Gas Furnace Pros and Cons
Here are some of the advantages and disadvantages of understanding Geothermal Heat Pump vs Gas Furnaces:
Advantages Of Geothermal Heat Pump
Energy efficiency
A GHP is a highly efficient heating and cooling system that can significantly reduce your energy consumption. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, a GHP can reduce your energy consumption by 25% to 50% compared to a conventional system. This is because a GHP utilizes electricity only to power the pump and fan rather than to generate heat. In fact, a GHP can produce four units of heat for every unit of electricity it consumes.
Environmental impact
Geothermal heat pumps (GHPs) are an excellent choice for reducing your carbon footprint, as they don’t release any greenhouse gases or pollutants, making them environmentally friendly. They use renewable energy from the earth, which can further reduce your emissions if you power them with renewable sources of electricity, such as solar or wind. Additionally, GHPs can improve indoor air quality as they don’t produce any combustion byproducts that can harm your health.
You can Also Learn More About Geothermal Heat Pump Maintenance For Optimal Performance.
Durability and maintenance
A Geothermal heat pump (GHP) is a long-lasting and dependable system with minimal moving parts and protection from the elements. A GHP can operate efficiently for 25 to 50 years, while the underground loop lasts more than 50 years. Compared to a gas furnace, a GHP requires less maintenance as it doesn’t need regular cleaning, tuning, or filter replacement.
Geothermal Heat Pump Cons
Initial cost
Geothermal heat pumps (GHPs) are generally more expensive than gas furnaces because they require drilling or digging to install the underground loop. The initial cost of a GHP can vary from $10,000 to $30,000, depending on the system’s size, type, and location. However, you can offset the initial cost by taking advantage of federal, state, and local incentives such as tax credits, rebates, and loans. Over time, you can also save money by reducing your energy bills and maintenance costs.
Space requirement
A Geothermal Heat Pump (GHP) needs enough land to install an underground loop. The amount of land required depends on the type of loop you choose: horizontal, vertical, or pond/lake. A flat loop needs more land than a vertical loop but is cheaper to install. A pond/lake loop requires access to a nearby water body but is the most efficient and least invasive option. You should also consider the soil and rock conditions as they affect the heat transfer and installation cost.
Don’t forget to learn more about Geothermal Heat Pump Vs Mini Split: Which One Is Better For You?
- High Energy efficiency
- Less Environmental impact
- Durability and maintenance
- Higher Initial cost
- Space requirement
Gas Furnace Pros
Initial Costs
When comparing gas furnaces to GHPs, gas furnaces are generally cheaper to install. This is because they do not require any excavation or drilling. The cost of a gas furnace can vary from $3,000 to $6,000, depending on factors such as its size, efficiency, and brand. Additionally, installing a high-efficiency gas furnace may make you eligible for rebates and tax credits.
Performance
Gas furnaces are a reliable and efficient option for home heating, particularly in colder areas. With the ability to reach temperatures up to 140 degrees Fahrenheit, they can produce powerful and consistent heat. In contrast, a Geothermal heat pump (GHP) can only reach a maximum temperature of 120 degrees Fahrenheit. Additionally, gas furnaces can quickly warm up your home, as they do not rely on the ground temperature.
Gas Furnace Cons
Energy efficiency
Gas furnaces are commonly used for heating homes but are less energy-efficient than geothermal heat pumps (GHP). Gas furnaces convert fuel to heat, and their efficiency is measured by annual fuel utilization efficiency (AFUE). The minimum AFUE for a gas furnace is 80%, which means that 20% of the fuel is wasted as exhaust. The highest AFUE for a gas furnace is 98%, which means that only 2% of the fuel is wasted. However, even a 98% efficient gas furnace is less efficient than a GHP, which can have an efficiency of over 300%.
Environmental impact
A gas furnace can have a severe impact on the environment because it releases greenhouse gases and pollutants that contribute to global warming and air pollution. Carbon dioxide, methane, nitrogen oxides, sulfur dioxide, and particulate matter are all emitted by gas furnaces, which can harm the environment and your health.
Durability and maintenance
A gas furnace is less durable and reliable than a geothermal heat pump (GHP). This is because it has more moving parts and is constantly exposed to weather changes. A gas furnace lasts 15 to 20 years, while a GHP lasts 25 to 50 years. Unlike a gas furnace, a GHP requires regular cleaning, tuning, and filter replacement to maintain optimal performance. Additionally, a gas furnace risks carbon monoxide poisoning, fire, or explosion if not properly installed, maintained, or vented.
- Lower Initial Cost
- Seemless Performance
- Lower Energy efficiency
- More Environmental impact
- Durability and maintenance
Geothermal Heat Pump vs Gas Furnace: Which One Should You Choose?
Choosing between a geothermal heat pump and a gas furnace depends on personal preferences, budget, climate, and home characteristics. Consider:
- Climate: In mild or moderate climates without freezing temperatures, a GHP efficiently handles heating and cooling with low environmental impact. In colder climates, a gas furnace provides powerful and consistent heating. Alternatively, a combination of GHP, a gas furnace, or a dual-fuel heat pump can be considered.
- Budget: A gas furnace is a more budget-friendly option with lower initial and installation costs. However, consider long-term costs, including energy bills, maintenance, and replacements. Despite higher upfront costs, a GHP can save money in the long run, and incentives can offset initial costs.
Don’t forget to learn more about Fan Coil Vs Heat Pump: A Guide To Choosing The Right HVAC System For Your Home
- Space: For large or rural properties, a GHP is suitable due to the ease of installing the underground loop. In contrast, a gas furnace is a space-saving option for small or urban properties without additional system space requirements. Consider the availability and cost of natural gas in your area.
- Environmental Impact: For an eco-friendly approach with a minimal carbon footprint, a GHP is preferable. It emits no greenhouse gases, utilizes renewable earth energy, and supports renewable electricity sources like solar or wind. In contrast, a gas furnace relies on non-renewable fossil fuels, negatively impacting the environment and health.
Geothermal Heat Pump vs Gas Furnace ~ Conclusion
Both a geothermal heat pump and a gas furnace are efficient heating and cooling systems for your house, but they offer distinct advantages and disadvantages. Your climate, money, available space, and environmental impact determine the best one for you. Before making a decision, examine the benefits and drawbacks of each system, as well as your preferences and home characteristics. You can also hire a professional contractor to assist you in selecting the best system for your home and installing it correctly and safely.