80 AFUE vs 96 AFUE: When heating your home, you want a reliable, comfortable, and energy-efficient furnace. But how do you know which furnace efficiency is best for your house? One of the most important factors to consider is the AFUE rating of the furnace. AFUE stands for Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency, and it measures how well a furnace converts fuel into heat. The higher the AFUE rating, the more efficient the furnace and the cheaper the heating bills. But is a higher AFUE rating always better? And how much can you save by choosing a 96 AFUE furnace over an 80 AFUE furnace? This blog post will answer these questions and help you decide which furnace efficiency suits your home.
What is AFUE?
Table of Contents
ToggleAFUE, or Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency, measures how efficiently a heating system converts fuel into usable heat annually. This is particularly relevant for furnaces and boilers. AFUE is expressed as a percentage, and a higher AFUE indicates greater efficiency. Homeowners can compare AFUE ratings to understand energy waste and potential fuel bill savings. However, it is essential to note that AFUE ratings vary based on fuel type, maintenance, and the specific heating system model. Remember that AFUE is just one factor to consider when comparing different furnaces. For example, a system with 96% AFUE converts 96% of fuel into heat, wasting only 4%.
Understanding 80 AFUE vs 96 AFUE with Factors
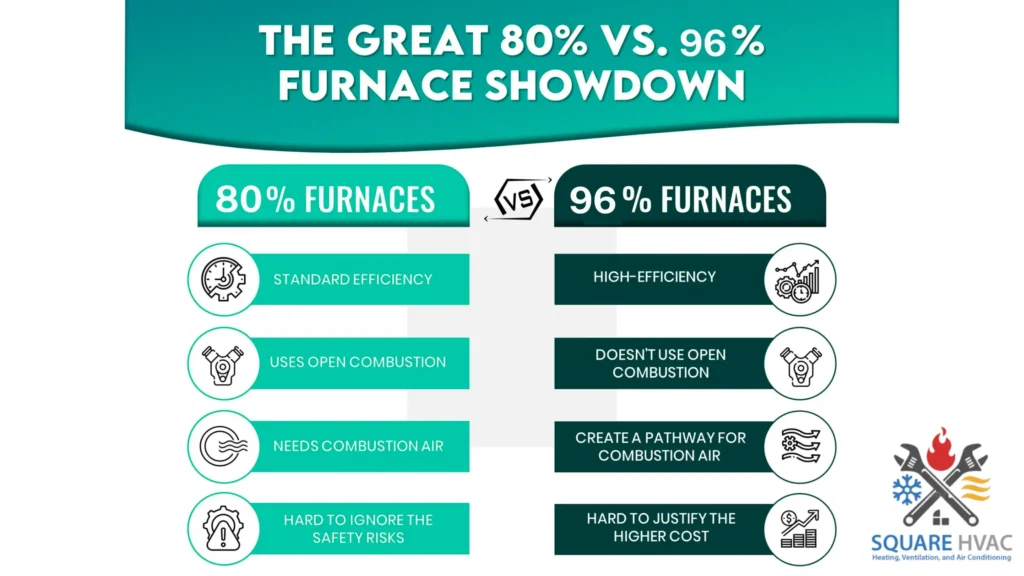
There are two main types of furnaces: 80 AFUE and 96 AFUE. The main difference between them is their fuel efficiency. A 96 AFUE furnace is more energy-efficient, which means it consumes less energy, reduces heating bills, and has a lower environmental impact.
However, the upfront cost of a 96 AFUE furnace is higher due to its 96% fuel-to-heat conversion efficiency, which wastes only 4%. Conversely, an 80 AFUE furnace converts only 80% of energy into heat, wasting 20%. If you’re comparing both furnaces, it’s essential to consider these factors to make an informed decision.
| Aspect | 80 AFUE | 96 AFUE |
| Definition | Conventional, affordable option | Condensing, efficient choice |
| Efficiency | Converts 80% of energy into heat | Converts 96% of energy into heat |
| Cost | Likely has a variable-speed blower | Higher upfront cost |
| Venting/Draining | Standard systems | Requires special venting/draining |
| Noise | May generate more noise | Likely incorporates noise-reduction technology |
| Heat Stages | Typically single-stage | Likely two-stage or modulating |
| Variable-Speed Blower | May have a fixed-speed blower | Likely has variable-speed blower |
| Benefits | Lower initial cost, suitable for specific scenarios | Higher efficiency, potential long-term savings |
80 AFUE vs 96 AFUE ~ Cost Comparison
The cost of a furnace depends on many factors, such as the brand, model, size, installation, and warranty. However, in general, a 96 AFUE furnace will cost more than an 80 AFUE furnace of the same size and type. According to HomeAdvisor, The average cost of a gas furnace ranges from $3,800 to $10,000, including installation, with a 96 AFUE furnace costing about $1,000 more than an 80 AFUE furnace. Of course, the exact price will vary depending on your location, contractor, and specific needs.
Saving Comparison
Choosing a 96 AFUE furnace over an 80 AFUE one can save significantly on heating bills. A 96 AFUE furnace consumes 16% less fuel, reducing energy usage and carbon emissions. Savings depend on climate, home size, fuel prices, and usage patterns. In simpler terms, a new 96 AFUE furnace could yield heating bills 16% lower than an 80 AFUE furnace. If you spend $100/month on winter heating, an 80 AFUE furnace could reduce costs to $80, while a 96 AFUE furnace might bring bills down to just $64, offering significant long-term savings.
Remember that these estimates may vary if replacing an older furnace, but even a modest 10-20% savings can make a noticeable difference in monthly expenses.
Heat Stages Comparison
AFUE ratings of 80 and 96 help distinguish furnaces. A single-stage furnace operates at total capacity whenever turned on, while a two-stage furnace offers variable capacity based on heating demand. Both ratings may feature different heat stages, but a 96 AFUE furnace is more likely to provide a two-stage or modulating heat stage, enhancing efficiency and comfort. Lennox, a well-known furnace manufacturer, states that all 96 AFUE furnaces have a two-stage or modulating heat stage, while 80 AFUE furnaces have only one stage.
You can also learn about Expansion Valve In Chiller: How It Works And Why It Matters
96 AFUE vs 80 AFUE ~ Safety Comparison
80 and 96 AFUE furnaces are safe if correctly installed, maintained, and vented. However, they differ in how they operate and vent the combustion gases. An 80 AFUE furnace is a conventional furnace that uses a metal flue to vent the hot exhaust gases outside. A 96 AFUE furnace condensing furnace uses a plastic pipe to vent the cooler and more acidic exhaust gases outside. A condensing furnace also has a secondary heat exchanger that extracts more heat from the exhaust gases, which makes it more efficient.
Noise-Reduction Technology
Furnaces can be noisy, but manufacturers use noise-reduction technology to minimize sound levels. This technology includes insulated cabinets, variable-speed blowers, sealed burners, and quiet venting systems. Furnaces with higher AFUE ratings, like the 96 AFUE furnace, are likelier to incorporate noise-reduction technology for a more tranquil user experience. Lennox, a leading furnace manufacturer, claims that all of its 96 AFUE furnaces feature SilentComfort™ technology, which reduces sound levels by up to 50%. An 80 AFUE furnace may not include this technology and could generate more noise.
Variable-Speed Blower
80 AFUE and 96 AFUE furnaces differ in the type of blower used. Variable-speed blowers offer better heating, humidity control, air quality, and energy efficiency. Fixed-speed blowers only have one speed, leading to uneven heating, poor humidity control, lower air quality, and higher energy consumption. According to Carrier, most 96 AFUE furnaces have variable-speed blowers, while some 80 AFUE furnaces only have fixed-speed blowers.
What Are the Benefits of a Higher AFUE Rating?
A higher AFUE rating offers several advantages.
Lower heating bills: A furnace with a higher AFUE rating produces more heat with less fuel, lowering energy consumption and heating costs. Upgrading to a new furnace with a 96% AFUE rating from an old furnace with a 56% AFUE rating can save up to $1,500 per year on heating bills.
Lower environmental impact: A furnace with a higher AFUE rating emits less carbon, reducing its contribution to global warming. Upgrading from an old furnace with 56% AFUE to a new one with 96% AFUE can reduce annual carbon dioxide emissions by 2.5 tons (source: U.S. Dept. of Energy).
Don’t forget to learn about Types Of Furnace Ignitors: An In-Depth Guide.
Higher comfort, safety, and air quality: A furnace with a higher AFUE rating has advanced features that make it more responsive, quieter, and cleaner. It also indicates a better venting system, reducing the risk of carbon monoxide poisoning.
When an 80 AFUE Furnace is Essential?
An 80 AFUE furnace may be better than a 96 AFUE furnace due to compatibility or budget constraints. The latter requires special and expensive venting and draining systems that may not be suitable for older or smaller venting systems. An 80 AFUE furnace is a good choice if a 96 AFUE furnace isn’t worth the investment. Although a 96 AFUE furnace can lead to long-term heating bill savings, it may not be worth the investment if you don’t plan to stay in your home for a long time or have more pressing expenses.
80 AFUE vs 96 AFUE ~ Conclusion
In conclusion, Choosing the proper furnace efficiency for your home can be challenging. An 80 AFUE furnace is affordable but may consume more fuel and produce more noise and emissions. A 96 AFUE furnace is efficient but may cost more upfront and require different venting and draining. Consult a professional contractor to assess your home and recommend the best furnace for your needs and budget.